Particulate nature of Matter
Matter :
Anything which occupy space and has a mass is called matter.
Example:
Air, Water, Oil, wood , Iron etc
Types of matter:
matter is basically of three types:
Solid:
Particles are held very close to each other in solids in a regular order and there is very little freedom of movement due to strong attractive forces between particles.
As a result, Solids have definite volume and definite shape.
Question: Write few examples of solids.
Challenge: Is Clay solid or liquid? Why is it solid or liquid?
Liquid:
Particles are close to each other but they can move around due to weaker attractive forces
between particles compared to solid particles.
As a result, Liquids have definite volume but do not have definite shape.
They acquire the shape of the container in which they are kept.
Question: Name 5 liquids. Is toothpaste a liquid?
Gas :
Particles are far apart their movement is easy and fast due to negligible attractive forces between particles. Gases have neither definite volume nor definite shape. They completely occupy the space in the container in which they are placed.
Question: Name 5 gases.
Challenge: Is gas or vapour same?
Why or why not?
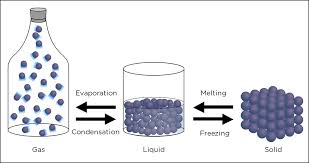
Inter-conversion of States of matter:
The states of matter are inter-convertible by changing the conditions of temperature and pressure.
On heating, a solid usually changes to a liquid, and the liquid on further heating changes to gas or vapour.
In the reverse process, a gas on cooling liquifies to a liquid and the liquid on further cooling freezes to the solid.
Sublimation: Sublimation is the change of solid state in to gaseous state without changing in to liquid. For example: Camphor, Ammonium chloride, Naphthaline.
Deposition: Deposition is the change of gaseous state into solid state. For Example gas deposition on water.
Read Law of conservation of mass examples
