PPT 3.1 Periodic table has the following keywords:Periodic Function,Groups,Periods,Valence,Alkali Metals,Alkaline Earth Metals,Transition Metals,Chalcogens,Halogens,Noble Gases,Lanthanoids And Actinoids.
This PPT 3.1 Periodic table aligns with the IB Diploma Chemistry Guide. It covers the past paper questions on this subtopic.
Objectives: This PPT enables the students to apply their learning to : Deduce the position of an element by using the electronic configuration vice versa.
Guidance: The students should know the above keywords. The IB recommended periodic table with group number 1 to group 18 is better to use.
Page Title
Exploring Unit 3.1: The Periodic Table of IB DP Chemistry
Dive into the world of Chemistry with our comprehensive guide to Unit 3.1: The Periodic Table of IB DP Chemistry! Learn all you need to know and become an expert at the topics here.
Do you want to understand the basics of Chemistry? If so, then get ready to explore the periodic table of IB DP Chemistry in Unit 3.1. This comprehensive guide will provide an in-depth introduction to the elements and properties that make up this essential part of the chemical world.
Understand the Organization of the Periodic Table.
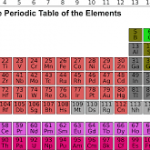
The periodic table of the elements is a graphic representation of known elements arranged according to their properties. Each element can be located in its appropriate place on the table based on its atomic number, which is equal to the number of protons in its nucleus. Elements in the same column, or group, have similar properties because they have the same number of valence electrons. Understanding how elements are organized and interact with one another can be key to solving chemistry problems.
Analyze the place of an element in the periodic table based on group and period
When analyzing the place of an element in the periodic table based on group and period, it is important to remember that elements within the same group share similar properties because they have the same number of valence electrons. Elements increase in atomic number down a group and across a period, while groups contain elements with roughly similar reactivity patterns. Modified versions of the periodic table can also be used to analyze an element’s properties such as electronegativity or ionization energy. By recognizing these trends when proposed with problems, IB DP Chemistry students can solve chemistry-related questions and understand how various elements interact with one another.
Examine Halogen and alkali metals Profiles and Trends in Reactivity.
Halogens are the 7th group on the periodic table and are located on the right hand side. Their outer shells always contain seven electrons , which gives them strong oxidizing properties that make them very reactive. Alkali metals, on the other hand, are first group elements, containing just one valence electron and all being very reactive metals. Their reactivity increases as you move down a group (similar to other metals) because an increasingly larger number of core electrons pull away at the valence electron, causing it to be more easily lost in reactions. By analyzing these trends in halogen and alkali metal reactivities, IB DP Chemistry students can further understand their reaction behaviors based on their position in the periodic table.
Investigate Oxidation States, Ionic Compounds, and Valency Principles
In this unit, students will also dive into the study of oxidation states, ionic compounds, and valency principles — all key concepts used to understand chemical reactions between molecules and elements. They will learn to identify relationships between the oxidation number of a compound or element in a reaction and its final products. This understanding of how various pieces of the periodic table interact with each other is essential for future scientific work.
You can look for chemistry IA templet here.
You can post your educational articles here on online educational magazine.
