Why Should You Care? Learn what it is and why it matters with this comprehensive guide! Discover how different elements can affect the strength of an atom’s pull and how to use this information.
Electronegativity is the ability of an atom to attract electrons to itself. It is an important property that helps determine the strength of chemical bonds, and is affected by the type of atom and its surrounding environment. By understanding it, you can make informed decisions about which elements are more likely to form strong covalent and ionic bonds.
What is Electronegativity?
It is a measure of an atom’s ability to attract electrons. The strength of the pull depends on both the type of atom and its surrounding environment. Atoms with greater electronegativity are more likely to form strong covalent and ionic bonds, while those with lower typically form weaker bonds and its Understanding can help you identify which molecules and chemical compounds are most stable.
The Periodic Table & Variations in Electronegativity.
The periodic table highlights how different elements can vary in their electronegativity. Generally, these differences between elements are due to the number of protons present in the nucleus. Atoms with more protons will have a greater pull and therefore higher electronegativity. Additionally, it is also affected by an element’s environment, such as if they are located near large atoms with strong pulls on electrons or areas of low electron density.
How Does the Atomic Structure from Each Element Affect Its Electronegativity?
The atomic structure of each element can significantly affect its electronegativity. In general, elements with more protons will have a greater pull and therefore higher electronegativity. This can be seen in the periodic table where elements further away from the sides tend to be more electronegative. On the other hand, elements located near large atoms or areas of low electron density may experience lower electronegativity due to the competition for electrons.
Electronegativity in Covalent Bonding.
Electronegativity plays an important role in covalent bonding between atoms. Covalent bonds are those in which two atoms share electrons rather than one atom transferring electrons to the other. The stronger the pull of the atomic nucleus, the more strongly the electrons will be drawn towards its center and shared with an adjacent atom. This means that elements with higher electronegativity can attract electrons more easily within a bond than those with lower ones. As such, it can be used to determine which chemical bonds will be formed and how strong they will be.
How Can You Use Electronegativity to Explain Chemical Reactions?
The concept can be used to explain why certain chemical reactions occur and why they favor one direction of the reaction. Since elements with higher electronegativity can attract electrons more strongly, they are more likely to draw electrons away from less electronegative elements. This results in a gradient of electronegativities across molecules, which when taken into consideration, can help explain why certain reactions occur at the atomic level.
Answer: It is the tendency of an atom to pull the shared pair of electron towards itself in a covalent bond.
Group 7/17 elements of periodic table are generally electronegative.
The 3 most electronegative elements are FON means Fluorine,Oxygen and Nitrogen.
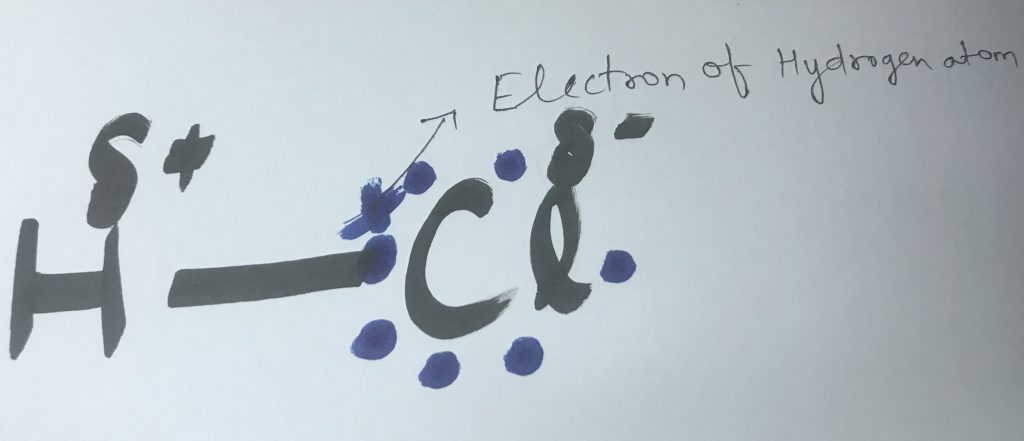
For Example: H-Cl molecule has polar covalent bond because Cl[chlorine] is more electronegative than H[hydrogen] so Cl pulls the electron pair towards itself and aquire partial negative charge and H acquires partial positive charge.